Describe a Teaching Plan for Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose
For the purpose of this lesson the. The patient will be able to perform self-monitoring of blood glucose using a blood glucose meter as evidenced by demonstration of the technique to the nurse.

Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose As Control Tool In The Different Management Contexts For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus What Is Its Current Role In Non Insulin Users
Touch the tip of the yellow window on the test strip.

. Blood glucose self-monitoring is indicated in most patients with insulin-treated diabetes but its value is limited unless users self-adjust their insulin dosage according to results. Insert the test strip into the glucose meter. Have each participant share hisher sample meal with the class and help them to identify the source of each of the macronutrients.
Have each person develop a self management goal related to eating. Patients should self-monitor their blood glucose at least four times a day before meals and before bed. Youll be able to see what makes your numbers go up or down such as eating different foods taking your medicine or being physically active.
Before meals and before taking insulin or medication Two hours after meals Before bedtime NoteFor people who may have low blood glucose reactions during the night a 300 AM blood glucose check may also be needed. Gently squeeze the end of your finger if necessary. To evaluate the contributions of an educational program for capillary blood glucose self-monitoring.
This helps you get a drop of blood. If you are taking insulin Self-monitoring your blood glucose. SMBG supports the management of hypoglycaemia hyperglycaemia illness and activityexercise.
When you see the flashing hour glass you have enough blood in the test strip. A quasi-experimental study performed in an outpatient unit of a tertiary health care service in a sample of 25 people with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus from July 2016 to December 2017 developed through interactive tools for care with capillary blood glucose. Read and write down the result in a logbook or store it in the glucose meter.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose SMBG is indisputable for people with type 1 diabetes. Simplifying pathophysiology medication usage blood glucose monitoring meal planning and overall management of the disease is daunting but it is a skill you can acquire with practice. It enables the individual to observe patterns of blood glucose results and adjust insulin doses accordingly.
Apply the blood to the test strip. Self monitoring of blood glucose or SMBG refers to home blood glucose testing for people with diabetes. Prick the end of a finger on the side.
Teach the patient that they need to monitor their blood glucoseThey need to call their primary care physician if they have blood glucose levels higher than their target for multiple days or if they have 2 readings of greater than 300 mgdL. Self-monitoring of blood glucose SMBG is an important component of modern therapy for diabetes mellitus. Self-monitoring of blood glucose SMBG levels is an integral part of treatment for everyone with Type 1 diabetes and access to blood glucose testing strips and meters and or flash glucose devices should not be restricted.
Teach the patient how to use their glucometer and record their results. Wait a few seconds the time varies by type of meter. Upon completion of lesson students will be have a clear understanding of diabetes mellitus complications involved and how to correctly monitor blood glucose levels using a glucometer.
A commonly recommended BGM plan Check blood glucose. Behavioral Objectives for the teaching plan The patient will be able to describe the diabetic medications that they are on and how to properly take the medication. Self monitoring is the use of regular blood testing to understand ones diabetes control and inform changes to improve ones control or wider regime.
SMBG has been recommended for people with diabetes and their health care professionals in order to achieve a specific level of glycemic control and to prevent hypoglycemia. Results need to be used by the PWD to make necessary changes to self-care. Teaching patients to take their prescribed medications correctly may be as important as the medication itself because without a good understanding patients may take it incorrectly with.
SMBG helps people using insulin to manage their glucose levels and identify low blood glucose levels before the development of severe hypoglycaemia. The goal of SMBG is to collect detailed information about blood glucose levels. It is arguably of less benefit in type 2 diabetes treated with diet alone or with oral medications where management is usually guided by HbA1c and is expensive.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose SMBG is an effective tool in the self-management of glucose levels in people with Type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes using insulin therapy and other medication that carries a risk of hypoglycaemia. Power Point presentation hand-outs glucometers including lancets and test strips alcohol pads 2x2 gauze pencils. Do not put blood on top of the test strip.
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the most important thing you can do to manage type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Create a plan to enhance diabetes self-management based on findings Background SMBG refers both to the act of checking blood glucose levels with a blood glucose meter and utilizing the results to make lifestyle and treatment regimen decisions. Use this as an opportunity to illustrate how favorite foods can be included each day.
Self monitoring of blood glucose levels has been a hotly disputed issue for a number of years particularly with. Self-monitoring of blood glucose blood pressure and having retinal screening carried out targeting goals tailored to individual need for example around footcare weight loss injection technique and self-monitoring activities applying sick day. Gently squeeze your finger to assist the flow of blood.
Insert the lancet into the lancing device. Test strip should be perpendicular to finger.
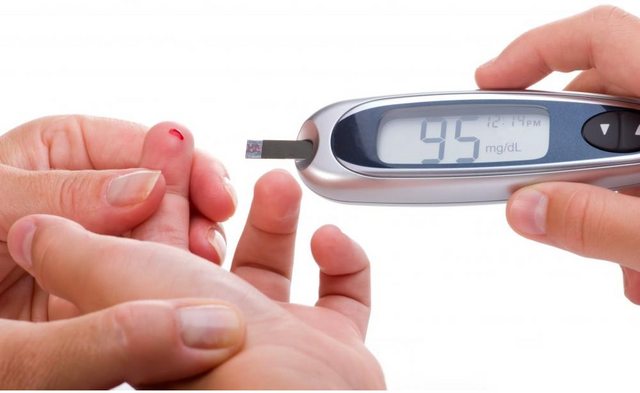
What Are The Steps Of Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose Smbg Dr Nikhil Prabhu S Blog Diabetes Care

Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose As Control Tool In The Different Management Contexts For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus What Is Its Current Role In Non Insulin Users
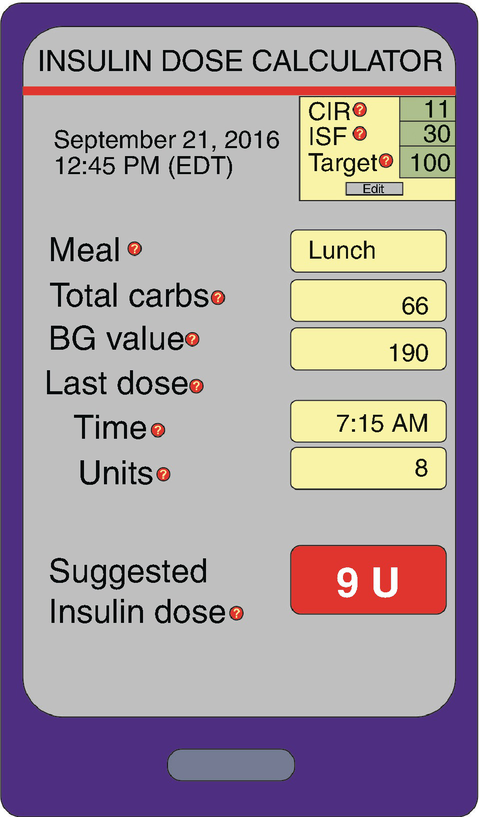
Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose As Control Tool In The Different Management Contexts For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus What Is Its Current Role In Non Insulin Users

Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Pdf Instruments For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose Comparisons Of Testing Quality Achieved By Patients And A Technician

Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Conceptual Framework Of Factors Influencing The Use Of Smbg Note A Download Scientific Diagram

Changes In Hba 1c Level Between Self Monitoring And Non Self Monitoring Download Scientific Diagram

Interventions For Endocrine Ppt Download

Pdf Factors Influencing Adherance To Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose Schedules Among Diabetic Patients

Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose
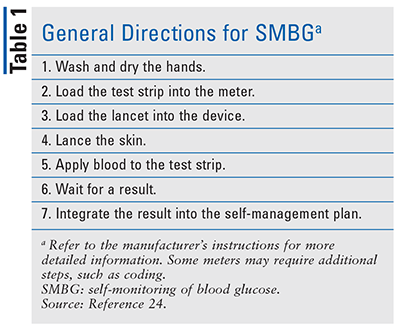
Unlocking The Full Potential Of Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Describe A Teaching Plan For Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose

Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose As Control Tool In The Different Management Contexts For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus What Is Its Current Role In Non Insulin Users

Pdf Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose In Type 2 Diabetes Systematic Review
Comments
Post a Comment